As the globe experiences an increase in digitization, conventional banking practices are rapidly losing relevance. Exploring open banking and ETL systems has brought about a substantial transformation in financial institutions, thus enabling greater transparency, competition, and innovation. This article delves into the concept of open banking, its significance, instances of available banking services, regulatory agencies and guidelines, security, and confidentiality considerations, the prospects of open banking, and the role of ETL in open banking data harmonization.
A Guide to Open Banking
Open banking is the practice of allowing third-party providers to access a bank’s customer data, with the customer’s permission. This data includes account balances, transactions, and other financial information, and it’s shared using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). [1]
Open banking is important because it encourages competition and innovation in the financial industry. When third-party providers access customer data, they can create new products and services, giving consumers more choices. This competition also forces traditional banks to improve their services and keep up with technology.
Open Banking Services Examples
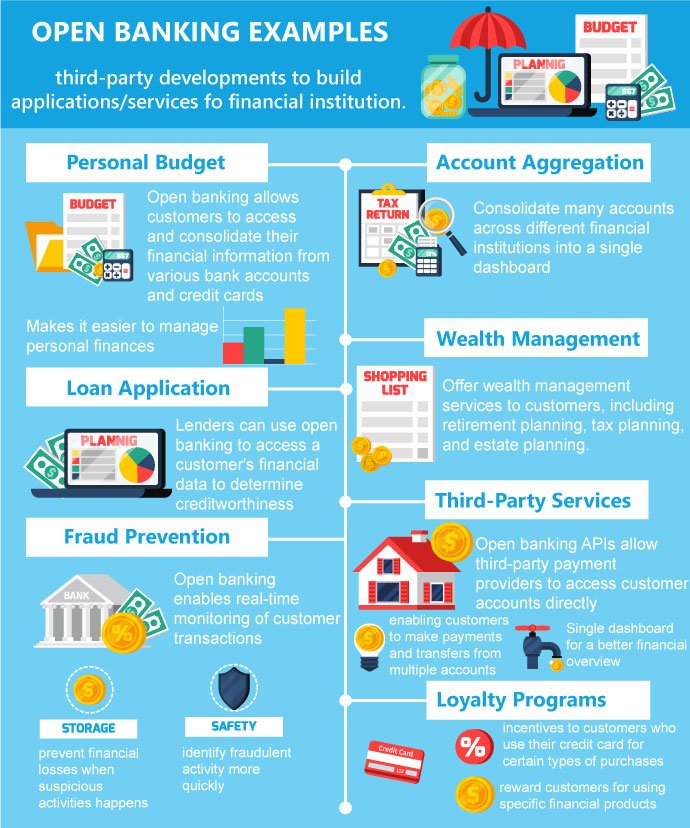
Open banking services provide many benefits, such as account aggregation, which allows customers to conveniently access their financial information in one central location, and payment initiation, which enables customers to directly transfer funds from their bank account without using third-party payment providers. This disruption to traditional banking practices has paved the way for new market entrants, like fintech firms, to offer various innovative products and services.
Open banking’s advantages extend beyond convenience and ease of access. The increased transparency it provides empowers customers to make more informed financial decisions. At the same time, the competition it fosters spurs traditional banks and new players alike to create more customer-centric offerings. Furthermore, open banking’s advanced security measures protect customers’ sensitive financial data.
With the advent of open banking, customers can benefit from a more streamlined and efficient financial management experience, free from the limitations of traditional banking services. As the trend towards open banking continues to evolve, the industry will see further advances in financial technology, enabling an even more comprehensive suite of offerings that cater to each customer’s unique needs.
Regulatory Landscape of Open Banking
The complexity of open banking regulations varies considerably from one country to another. Diverse regulatory agencies, such as the European Banking Authority (EBA), the Open Banking Implementation Entity (OBIE) in the UK, and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) in the US, are accountable for open banking oversight.
Compliance standards that banks and fintech must follow include obtaining the customers’ consent before data sharing, verifying the accuracy and currency of data, and allowing customers to revoke their consent whenever they want. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict data collection, utilization, and storage procedures for customer data.
Innovation and Security
Although open banking offers numerous advantages, it also poses essential security and privacy concerns. The security risks associated with open banking include hacking, phishing, and identity theft. Therefore, adopting effective measures like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and periodic security audits is crucial to guarantee security and privacy.
Apart from security, data sharing and consent are equally significant factors that require attention. Banks and fintech firms must ensure that their customers comprehend the implications of data sharing and receive precise details regarding how their data will be used.
Importance of Data Harmonization in Open Banking
Now that we have covered the basics of Open Banking, its importance, and the regulations and standards that govern it, let’s dive deeper into the role of ETL in Open Banking data harmonization.
What is ETL?
Data warehousing and integration rely on ETL, which involves extracting data from various sources, transforming it into a suitable format for analysis, and loading it into a target system.
The Open Banking industry recognizes the importance of ETL in harmonizing and integrating data from diverse sources. Using ETL makes it possible to create a comprehensive view of a customer’s financial information.
Importance of Exploring Open Banking with ETL
Exploring Open Banking with ETL is a practice that involves the exchange of customer information between multiple financial institutions. The data must be uniform and compatible across various systems and platforms to facilitate this exchange.
To ensure that the data is consistent and precise across different systems, ETL plays a pivotal role in the data harmonization process for Open Banking. ETL functions by extracting data from various sources, transforming it to meet the necessary standards, and loading it into the intended systems.
ETL’s contribution to the Open Banking data harmonization process cannot be understated. Ensuring the data is uniform, and error-free leads to enhanced data quality, reduced errors, and more accurate analysis and reporting.
Challenges in Integrating Open Banking Data
Incorporating Open Banking data can prove daunting, mainly due to financial information’s intricate and diverse nature. Financial data often comes in distinct structures across various systems, making it arduous to map and standardize data elements.
Moreover, Open Banking data can be subjected to distinct regulatory obligations, creating a significant obstacle in ensuring compliance across multiple platforms and systems.
To address these challenges, financial institutions must adopt robust strategies to enable the seamless integration of Open Banking data. These strategies should involve using advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, ETL-Tools, and machine learning to streamline data mapping and standardization processes.
Best Practices for Exploring Open Banking with ETL
For exploring open banking with ETL, it is important to follow best practices. These include:
- Data validation and cleansing: Validate and cleanse data to ensure that it is accurate, complete, and consistent.
- Standardization of data formats: Standardize data formats to ensure that data can be integrated and harmonized across different systems.
- Integration with other systems: Integrate ETL processes with other methods to ensure seamless data transfer and harmonization.
- Automation and monitoring: Automate ETL processes where possible to reduce errors and increase efficiency. Monitor ETL processes to ensure they are running smoothly and identify issues quickly.
ETL Best Practices for Open Banking Data Harmonization
To ensure successful data harmonization in Open Banking, following best practices in the ETL process is crucial. ETL is the process of extracting data from various sources, transforming it to meet specific requirements, and loading it into the target system. In Open Banking, ETL is vital in integrating data from multiple sources and making it usable for different applications. Here are some best practices for ETL in Open Banking:
Data validation and cleansing
Before extracting data, it’s crucial to validate and cleanse it to ensure its quality and accuracy. Data cleansing involves removing any irrelevant or duplicate data, fixing formatting issues, and ensuring that the data is consistent across all sources. Data validation ensures that the data meets specific standards and requirements.
Standardization of data formats
Different systems may use other data formats, making it challenging to integrate them. Standardizing the data format ensures that data is consistent across different systems, making it easier to blend.
Integration with other systems
To achieve optimal data harmonization, integrating ETL processes with other systems within the organization is crucial. This integration facilitates the seamless flow of data across multiple systems, which minimizes the chances of errors and guarantees that everyone is working with consistent data.
Automation and monitoring
Optimizing the ETL process for efficiency demands maximum automation, minimizing error risks, and ensuring replicability. Besides, scrutinizing the ETL process in real time can detect anomalies and quick fixes to unforeseen issues.
Video
Did you read the blog but are still unsure what it means? We’ve got you covered with a great explainer video that breaks it down simply!
Open Banking is all about giving you more control over your financial data and empowering you to make more informed decisions about your money.
Future of Open Banking
As Open Banking continues to gain traction, its future is rife with potential developments and trends. One such trend is the proliferation of fintech startups and other non-traditional players, providing groundbreaking Open Banking services. This could introduce a new era of competition and choice for consumers and create possibilities for banks and fintech to collaborate and form partnerships. With the development and harmonization of regulatory frameworks, Open Banking could also gain widespread global acceptance and adoption. As data sharing through Open Banking increases, we might witness the emergence of new products and services that utilize this data, such as tailor-made financial guidance and cutting-edge risk management tools. Ultimately, the future of Open Banking will be shaped by many factors and will be very exciting.
Conclusion
The traditional banking industry faces significant disruption with the emergence of Open Banking, paving the way for more innovative collaborations between fintech and established banks. However, the success of Open Banking hinges on tackling the challenges and opportunities inherent in the ETL process. Harmonizing data is crucial to the proper functioning of Open Banking, and the ETL process must be executed with precision to enable seamless data flow across various systems. Adopting best practices like data validation, cleansing, standardization, integration, and automation can empower banks and fintech to leverage Open Banking to its fullest potential.

